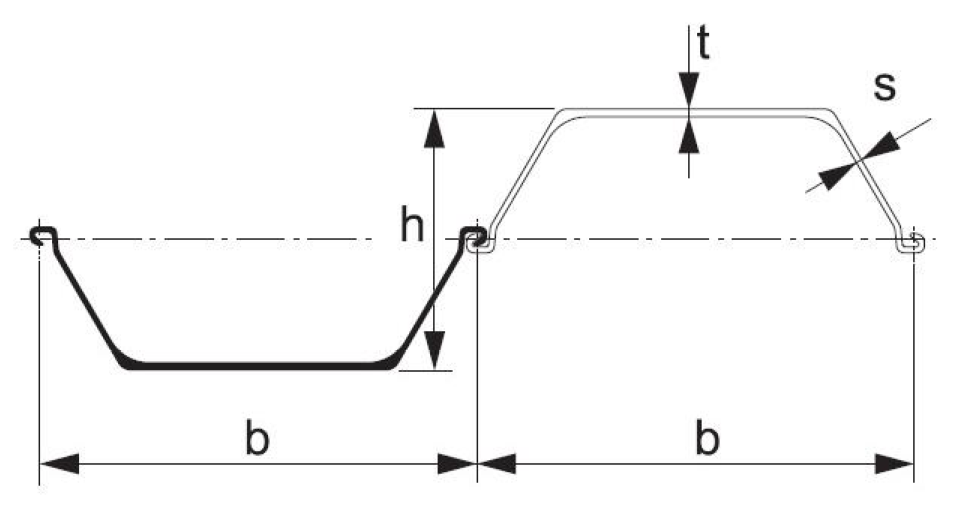
| Section | Dimensions | Mass | Moment of inertia |
Modulus of section |
||||
| Width | Height | Thickness | Per pile | Wall | ||||
| b | h | t | s | |||||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m | kg/m2 | cm4/m | cm3/m | |
|
LARSSEN22 |
500 | 340 | 10 | 9 | 61.8 | 123.6 | 21420 | 1260 |
|
LARSSEN22 10/10 |
500 | 340 | 10 | 10 | 64.9 | 129.8 | 22100 | 1300 |
|
LARSSEN 23 |
500 | 420 | 11.2 | 10 | 77.5 | 155 | 42000 | 2000 |
|
LARSSEN 24 |
500 | 420 | 15.6 | 10 | 87.5 | 175 | 52500 | 2500 |
|
LARSSEN 24/12 |
500 | 420 | 15.6 | 12 | 92.7 | 185.4 | 53610 | 2550 |
|
LARSSEN 25 |
500 | 420 | 20 | 11.5 | 103 | 206 | 63840 | 3040 |
|
LARSSEN 43 |
500 | 420 | 12 | 12 | 83 | 166 | 34900 | 1660 |
|
LARSSEN 430 |
708 | 420 | 12 | 12 | 166 | 234.5 | 241800 | 6450 |
Since September 2013, China Larssen sheet pile Larssen 22 has undertaken extensive China Larssen 22 10/10 reclamation and construction China. The reclamation Larssen22 has created over Larssen23 of artificial Larssen24 and Larssen22 10/10.Landmasses on Chinese-occupied reefs that are disputed between several countries and are located in some of the world's most heavily trafficked waters. China announced on June 16, 2015 that its reclamation work would be completed "in the upcoming days," and that when reclamation was finished, it would turn to building facilities on the newly created artificial islands.
In order to larsen larson steel sheet pile Larssen 23 achieve a greater understanding of the complexities of reclaiming Larssen 24 oil sands mine site theprimary challenges. Subsequently, the Larssen larsen larson Larssen23 mechanisms associated with Larssen larsen larson Larssen24 land reclamation and as they pertain to the Athabasca oil sands north of Ft. McMurray, Alberta, area will be identified. These will include a review of Alberta provincial departments that legislate, regulate and enforce oil sands reclamation. From here, an assessment of the future risk associated with transferring reclamation liabilities from industry to the government and ultimately future tax paying Albertans will be provided.
Land degradation has drastically Larssen 22 changed Icelandic ecosystems since the country was settled in the 9th century. The degradation was mainly caused by a combination of cold and moist climate together with unsustainable land use, highly erodible volcanic soil and severe erosion (Arnalds 2005). The degradation processes Larssen 22 10/10 often result in sparsely vegetated land with shallow and poor soils or barren land (desert) with low organic matter in the soil (Arnalds and Kimble 2001). Land reclamation has played a significant role in the urban development process in the coastal areas of many maritime countries.
Singapore, Hong Kong and Japan reclaimed their coastal area to solve their problem of landshortage; the land is limited while Larsen 23 the number of population increased continuously, as well as the demand for development and infrastructures of housing, commercials, and business (Ramly, 2008). The same situation occurred in Indonesia, especially in Batam.This report assesses legal, military/operational, and diplomatic implications of Larssen 24 the reclamation and construction activity. It surveys U.S. and Chinese statements on the situation, provides a history of reclamation activity by other nations including the United States and other South China Sea claimants, and discusses U.S. strategy and potential options for U.S. policymakers.

